
In today’s digital ecosystem, Security Protocols are no longer optional—they are essential. Every enterprise, from startups to global corporations, must defend against cyberattacks, data breaches, compliance violations, and insider threats. As technology evolves, so do vulnerabilities. This has prompted a shift from reactive security to proactive enterprise risk management, where Security Protocols act as the backbone of organizational defense strategies.
Traditionally, IT risk management focused on firewalls, antivirus, and perimeter security. However, modern threats such as ransomware, sophisticated phishing campaigns, cloud misconfigurations, and zero-day exploits require advanced Security Protocols that can protect data, infrastructure, applications, and users at scale.
Top 5 Enterprise Security Protocols Changing IT Risk Management, why they matter, how they work, and how organizations can implement them to protect assets while maintaining agility and innovation.
Why Enterprise Security Protocols Matter
Before discussing specific Security Protocols, it is important to understand why they are critical to IT risk management.
1. From Perimeter Defense to Zero Trust
Legacy approaches assumed that everything inside a corporate network was trustworthy. Modern threats have invalidated this assumption. Today, attackers can originate from within networks, exploit trusted third-party services, or bypass firewalls. Modern Security Protocols shift defenses to identity, behavior, encryption, and continuous validation rather than perimeter alone.
2. Regulatory Compliance and Audits
Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX require strict data protection rules. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Robust Security Protocols help organizations meet regulatory requirements and demonstrate compliance during audits.
3. Protecting Distributed Workforces
Remote work, cloud services, and hybrid environments are now standard. This increases the attack surface and eliminates traditional network boundaries. Enterprise Security Protocols provide consistent security across distributed users, devices, and systems.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
Security Protocols generate logs, alerts, and analytics that provide visibility into threats, vulnerabilities, and patterns. These insights help decision-makers prioritize risk mitigation, optimize investments, and reduce response times.
5. Business Continuity and Resilience
A single breach can disrupt operations, cause financial losses, and erode customer trust. Implementing strong Security Protocols enhances organizational resilience by ensuring continuity even under attack.
Understanding these motivations helps frame how important Security Protocols are in modern IT risk management. Now let’s explore the top five protocols that are transforming how enterprises secure assets in 2025 and beyond.
1. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
What Is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust Architecture is an advanced Security Protocol that assumes no entity—inside or outside the network—can be trusted by default. Unlike traditional models, Zero Trust enforces strict identity verification for every access request, every transaction, every session.
Instead of “trust but verify,” ZTA requires “never trust, always verify.”
Core Principles
- Least Privilege Access
Users and systems are granted the minimal permissions required to perform tasks. This limits lateral movement if compromised. - Continuous Authentication and Authorization
Every access request is re-verified in real time using identity, context, and risk signals. - Micro-Segmentation
Networks and systems are divided into isolated zones, reducing the blast radius of attacks. - Device and Behavioral Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of device posture and user behavior adds additional context to security decisions.
Why Zero Trust Is Changing IT Risk Management
Zero Trust is a cornerstone Security Protocol for modern enterprises because:
- It reduces the risk of insider and lateral attacks.
- It protects cloud and on-premise systems uniformly.
- It integrates with multi-factor authentication (MFA), identity providers (IdP), and least-privilege policies.
- It provides dynamic access control that adapts to real-time risk.
For example, a login from a trusted location might be granted access with minimal friction, while the same access attempt from a foreign country might trigger step-up authentication. ZTA transforms access control from static to intelligent.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing Zero Trust is not trivial. It requires:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) integration
- Micro-segmentation planning
- Real-time analytics
- Behavioral monitoring
Despite the complexity, Zero Trust is one of the most effective Security Protocols for reducing risk in hybrid and cloud environments.
2. Secure Sockets Layer and Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS)
What Are SSL and TLS?
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS), are foundational Security Protocols used to encrypt data in transit. They ensure that communication between clients and servers remains confidential and tamper-proof.
TLS has replaced SSL in most modern systems due to enhanced security and cryptographic improvements.
How SSL/TLS Works
- Handshake Process
Client and server negotiate encryption parameters through a handshake. - Public/Private Key Exchange
Certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs) validate server identities. - Symmetric Encryption
Once the connection is established, symmetric keys secure data exchange.
Why SSL/TLS Matters
SSL/TLS is one of the most widely used Security Protocols because:
- It protects sensitive data such as passwords, credit card numbers, and user information.
- It builds trust with users through HTTPS indicators in browsers.
- It prevents man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
- It is required for compliance with regulations like PCI DSS.
Real-World Application
Every modern website and API uses TLS. From online banking platforms to enterprise APIs and mobile applications, TLS ensures encrypted communication between endpoints.
Best Practices
- Use strong cipher suites and up-to-date certificates
- Implement HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
- Monitor certificate expiration and revocation
- Ensure perfect forward secrecy (PFS) support
In the era of APIs, remote services, and IoT, SSL/TLS remains one of the most essential Security Protocols for protecting data in motion.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
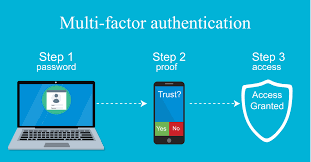
What Is MFA?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances login security by requiring two or more verification factors beyond just a username and password. It combines:
- Something you know (e.g., password)
- Something you have (e.g., mobile device, token)
- Something you are (e.g., biometric data)
MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access—even if a password is compromised.
Why MFA Is a Critical Security Protocol
Passwords alone are weak due to:
- Reuse across sites
- Susceptibility to phishing
- Brute-force attacks
- Credential stuffing
MFA and modern authentication protocols like FIDO2 transform access control by making it significantly harder for attackers to impersonate legitimate users.
Common MFA Methods
- SMS/Email One-Time Passcodes (OTP)
- Authenticator apps (e.g., Microsoft Authenticator, Google Authenticator)
- Biometric verification (fingerprint, facial recognition)
- Hardware tokens (e.g., YubiKey)
Impact on IT Risk Management
By requiring multiple factors, MFA:
- Prevents unauthorized access even with stolen credentials
- Protects administrative and privileged accounts
- Reduces helpdesk costs due to fewer password resets
- Helps meet compliance frameworks like NIST, GDPR, and HIPAA
Adoption Considerations
While MFA is highly effective, enterprises should:
- Avoid SMS as a sole factor due to SIM-swap risks
- Use risk-based authentication for context-aware access
- Educate users to reduce push-fatigue attacks
- Deploy seamlessly across devices and applications
MFA is one of the most impactful Security Protocols organizations can implement for robust identity protection.
4. OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC)
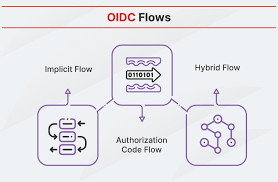
What Are OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect?
OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC) are widely adopted authorization and authentication Security Protocols used to secure access to APIs and services.
- OAuth 2.0 focuses on authorization — allowing applications to access user resources without exposing credentials.
- OpenID Connect extends OAuth 2.0 to handle authentication — verifying user identity securely.
These protocols enable seamless and secure delegation of access between applications.
How They Work
OAuth 2.0 enables users to log into third-party applications without sharing passwords. For example, signing into a service with “Sign in with Google” uses OAuth 2.0 to grant limited access.
OIDC adds an identity layer that lets applications verify user profiles and authenticate sessions securely.
Why They Matter
OAuth 2.0 and OIDC are leading Security Protocols in API security and modern application architecture because:
- They decouple authentication from resource access
- They support token-based access instead of credentials
- They integrate with identity providers like Azure AD, Google Identity, and Okta
- They help avoid password-based exposure
In microservices and serverless architectures, token-based protocols are essential for securing APIs and services without compromising performance.
Security Enhancements
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens) for secure token exchange
- Scopes and claims for fine-grained access control
- Refresh tokens for long-lived sessions without re-authentication
- PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) for enhanced security
OAuth 2.0 and OIDC are foundational Security Protocols that enable modern digital ecosystems to scale without sacrificing identity and access protection.
5. Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
What Is S/MIME?
S/MIME is a Security Protocol designed to secure email communication using encryption and digital signatures. It ensures:
- Confidentiality — Email content is unreadable by unauthorized parties
- Integrity — Content cannot be altered without detection
- Authenticity — Digital signatures validate sender identity
What Is PKI?
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) underpins S/MIME and many other encryption protocols. It manages digital certificates, key pairs, and certificate authorities (CAs) to establish trust across networks.
Why These Protocols Matter
While email is a longstanding technology, it remains a significant attack vector for phishing, spoofing, and data leaks. S/MIME and PKI ensure secure business communication by:
- Preventing email tampering
- Protecting sensitive information in transit
- Establishing digital identities within enterprises
- Supporting secure document signing and encryption
In regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and legal sectors, these Security Protocols are essential for compliance and secure communications.
Implementation in Modern IT
Enterprises implement S/MIME and PKI to:
- Encrypt internal and external email communication
- Sign emails to verify sender authenticity
- Manage certificates centrally with automated lifecycles
- Integrate with email clients like Outlook and Gmail
These protocols remain critical contributors to enterprise security strategies and risk management frameworks.
How Security Protocols Improve IT Risk Management
The five protocols discussed above work together to strengthen IT defenses:
- Zero Trust redefines trust decisions based on identity and context
- SSL/TLS encrypts data in motion across networks
- MFA secures user identities and access points
- OAuth/OIDC protects API access and authentication
- S/MIME/PKI ensures secure communications and trusted identities
Together, they form a multi-layered defense strategy that reduces the attack surface, improves visibility, and enhances incident response.
Best Practices for Implementing Enterprise Security Protocols
To maximize the impact of Security Protocols, enterprises should follow strategic practices:
1. Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Evaluate configurations, gaps, and compliance with frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST, and CIS benchmarks.
2. Centralize Identity and Access Management
Use platforms like Okta, Azure AD, or AWS IAM to manage authentication, policies, and devices consistently.
3. Monitor and Log Everything
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems help detect abnormal behavior and speed up threat response.
4. Automate Certificate and Key Management
Implement lifecycle automation to avoid expired certificates and reduce operational overhead.
5. Educate Users on Security Hygiene
Even the best Security Protocols fail if users are phished or misuse credentials. Regular training reduces risk.
Challenges and Considerations
While Security Protocols are powerful, they also present challenges:
- Complexity in implementation and integration
- The need for ongoing monitoring and updates
- Balancing security with usability
- Coordinating policies across cloud and hybrid environments
Successful risk management requires aligning Security Protocols with the organization’s goals, resources, and threat landscape.
Future Trends in Security Protocols
Security Protocols continue to evolve with emerging technologies such as:
- AI-driven anomaly detection for adaptive responses
- Post-quantum cryptography to prepare for quantum threats
- Behavioral biometrics for continuous authentication
- Decentralized identity systems for enhanced privacy
Enterprises must stay current to ensure resilience against the next generation of cyberattacks.
Conclusion
Effective IT risk management no longer depends on isolated defenses but on a holistic strategy built upon strong Security Protocols. By implementing advanced protocols such as Zero Trust, SSL/TLS, MFA, OAuth/OIDC, and S/MIME/PKI, organizations can protect data, identities, and infrastructure in a world of rapid digital transformation.
These protocols do more than secure systems—they enable trust, drive compliance, and enhance business continuity. As threats evolve, so must enterprise security frameworks. The right Security Protocols empower organizations to navigate uncertainty with confidence and deliver secure, seamless experiences for customers and employees alike.
Want to know about “Top 5 Chatbot Platforms Every Company Should Use“

